Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming more popular in the United States. Knowing about EV charging stations is key. A strong charging infrastructure supports green transportation and makes electric vehicle charging easier. This guide will explain the types of EV stations, their costs, and their role in sustainable energy.
Companies like Legrand are making charging solutions better for everyone. We’ll explore EV charging stations in more detail. We’ll see why they’re important and how technology is helping this industry grow.
Key Takeaways
- Electric vehicles are growing in popularity, necessitating a stronger charging infrastructure.
- Different types of charging stations cater to varied needs and charging speeds.
- Public and residential chargers support the shift towards sustainable transportation.
- Understanding the costs associated with charging can help EV owners plan better.
- Tools for locating EV stations make it easier for drivers to find charging options.
Understanding Electric Vehicle Charging
Charging electric vehicles is key for EV owners. There are many ways to recharge, based on what’s convenient and what’s available. You can choose from Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging. Each has its own benefits, depending on how you use your car.
Level 1 charging is simple. It uses your home’s standard outlets. It adds 6 to 8 kilometers of range per hour. This is great for charging overnight at home, as it’s slow but works well for those who don’t need to charge fast.
Level 2 charging is faster. You’ll find these stations in public spots, workplaces, and homes. They charge your car faster, so you can leave with more range.
DC Fast Charging is the fastest option. It’s found at over 1,000 stations in the U.S., run by EVgo. It can charge your car up to 80% in a short time. This is perfect for long trips, where quick charging is a must.
The Combined Charging System (CCS) is now the standard for charging. Companies like Legrand make products that work with these standards. This makes it easier for people to find charge ports wherever they go.
As more people drive electric cars, the need for charging spots is growing. By 2030, there could be 350 million electric vehicles. Knowing your charging options helps you choose what’s best for you, whether you’re at home or on the road.
The Importance of EV Charging Stations in the US
The growth of electric vehicles (EVs) depends a lot on charging stations. By December 2023, the US had over 165,000 public charging ports. This shows a big step forward in charging stations infrastructure.
Charging stations are key for both personal and fleet use. Without them, moving to green energy would be hard.
Less than 1% of public EV charging ports are Level 1. Almost 80% are Level 2. DC fast chargers make up over 20% of stations. These options help speed up EV adoption everywhere.
Experts say we need more public EV charging stations. S&P Global Mobility thinks we’ll need about 1.2 million Level 2 chargers by 2027. By 2030, we’ll need almost twice that.
But, not all areas have enough charging stations. This creates ‘charging deserts’ where people can’t charge their EVs. This problem makes it hard to switch to green energy.
To fix this, we need to invest in more charging stations. The Biden Administration plans to spend $7.5 billion on EV chargers. They aim to build at least 500,000 public chargers by 2030.
In short, without enough charging stations, EVs might not grow. We need better charging stations infrastructure for a greener future.
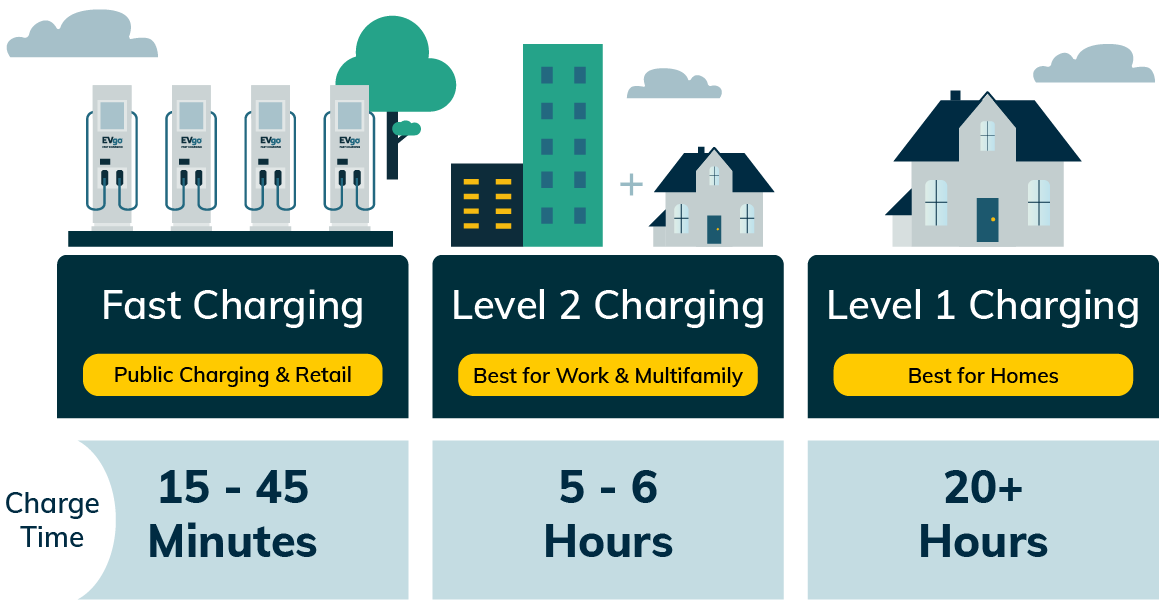
Types of EV Charging Stations
Electric Vehicle (EV) owners have many charging options. Each type is suited for different needs and situations. Knowing about Level 1, Level 2, and DC fast charging helps find the best option for your car and lifestyle.
Level 1 Charging
Level 1 charging uses a standard 120-volt outlet, perfect for home use. It charges slowly, adding up to 5 miles of range per hour. It takes about 8 to 12 hours to fully charge an EV, but it’s great for overnight charging if you drive short distances.
Level 2 Charging
Level 2 charging works at 240 volts, charging faster than Level 1. You can find it in public spots and homes. It adds about 25 miles of range per hour, with power from 7 kW to 22 kW. Most EVs, except Tesla, use the J1772 connector for Level 2 charging. Brands like BMW and Volkswagen use the CCS (SAE Combo) connector.
DC Fast Charging
DC fast charging is the quickest option. It can add up to 250 miles of range per hour. These stations can charge an EV to 80% in about 20 to 30 minutes. DC chargers have power from 50 kW to over 100 kW. Different connectors are used, like CHAdeMO for Nissan and Mitsubishi, and Tesla Supercharger for Tesla vehicles.

| Type of Charging | Voltage | Range Added per Hour | Charging Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Charging | 120 V | Up to 5 miles | 8 to 12 hours |
| Level 2 Charging | 240 V | Up to 25 miles | Varies by charging station |
| DC Fast Charging | 50 kW and above | Up to 250 miles | 20 to 30 minutes for 80% |
How EV Charging Stations Work
It’s important for EV owners and operators to know how charging stations work. These stations change AC power from the grid to DC power for the car’s battery. This can happen through the car’s charger or the station itself, making charging faster.
Charging stations have different EVSE ports and connectors for various cars. The SAE J1772 connector is common for Level 2 chargers in North America. DC fast chargers use CCS, CHAdeMO, and Tesla connectors.
As more electric cars hit the roads, it’s key to grasp the role of charging tech. Level 1 chargers add 5 miles of range per hour. Level 2 chargers, which are more common, can add up to 20 miles per hour. This suits most drivers who charge at home.
DC Fast Chargers are a big deal, adding 80 miles of range in 20 minutes. Businesses need to invest in both the hardware and software for these stations. Proper installation at public spots boosts sustainability, loyalty, and attracts customers.
| Charger Type | Charging Speed (Miles per Hour) |
|---|---|
| Level 1 Charger | Up to 5 miles |
| Level 2 Charger | Up to 20 miles |
| DC Fast Charger | 80 miles in 20 minutes |
Efforts like Efficiency Maine’s funding help grow charging infrastructure. As technology advances, so does the availability of EV charging. This ensures drivers can meet their charging needs efficiently.
Finding EV Charging Stations Near You
Finding a charging station nearby is key for electric vehicle owners. Many tools make it easy to locate charging stations. These tools help drivers find the right charging spot, making charging smoother.
Using Charging Station Locator Tools
Many apps and websites help find charging spots. GRID.com, for example, lists stations across the U.S. Users can filter by speed, availability, and vehicle type. It shows over 160,000 public stations’ status in real-time.
The GRID app also shows if stations are available and what plugs they have. It’s great for both long trips and daily drives. ChargePoint and Electrify America offer fast charging, making it even easier to find a spot.
Community Resources for EV Charging
Local efforts are key in making EV charging more available. Many projects add stations, helping more people charge at home. The government aims to add 500,000 stations by 2024, making it even better for EV users.
As more stations are added, the need for them grows. Knowing what’s available in your area helps everyone. It’s good for both you and your community as more people switch to electric.
| Charging Network | Number of Stations | Type of Charging |
|---|---|---|
| GRID.com | 160,000+ | Level 2, Level 3 |
| PlugShare | 140,000 | Level 2, Level 3 |
| ChargePoint | Largest Network | Multiple Levels |
| Electrify America | Second Largest Network | Level 3 Fast Charging |
EV Charging Station Costs and Pricing Models
Knowing about EV charging costs is key for both personal users and businesses thinking about installing charging stations. The cost of electric vehicle charging can change a lot. This depends on the charging level, installation needs, and where the station is. Looking into these areas helps us understand the average cost of charging an EV and the different pricing models today.
Factors Influencing Charging Costs
Many factors influencing costs affect the charges when using electric vehicle charging stations. Important things to consider include:
- Charging Level: Different chargers charge at different speeds and cost differently. Level 1 chargers are cheaper, with prices from $200 to $1,000. Level 2 chargers start at $1,500 and can go up to $5,000. High-speed DC fast chargers (Level 3) are the most expensive, starting around $20,000 and possibly reaching $200,000 with setup and upkeep.
- Electricity Rates: Electricity prices change based on where you are and when you charge. Public charging usually costs more than charging at home.
- Charging Speed: Faster chargers, like DC fast charging, cost more because they need more infrastructure and can have higher demand charges.
- Infrastructure and Installation: Commercial installations need infrastructure upgrades, which can cost between $12,000 and $15,000 on average. This adds to the overall cost.
Average Cost of Charging
The average cost of charging an EV depends on the setup and electricity rates. Home charging is usually cheaper than public stations. Public station fees vary a lot based on the pricing model used:
| Pricing Model | Description |
|---|---|
| Per kWh Pricing | Charges based on the amount of electricity used, common for most public charging stations. |
| Time-Based Pricing | Charges users based on how long they charge, good for slower chargers. |
| Flat Rate Subscription | A fixed monthly fee for unlimited charging, great for those who charge often. |
Investing in EV charging stations can save money in the long run if planned well. There are often incentives and rebates at state, local, or federal levels. Understanding these points helps make better financial choices when using or setting up charging networks.
Installation of EV Charging Stations at Home
Getting a home charging station for your electric vehicle is a smart move. It makes charging easier and saves money. First, check if your home’s electrical system can handle it. This is key for home charging installation.
Some homes might need a panel upgrade or a load-management system. This ensures your electrical panel can support the charger.
Picking the right EV charger is important. Level 1 chargers are cheaper but charge slower. Level 2 chargers are faster and more efficient. Legrand charging solutions offer reliable options for modern electric vehicles.
After choosing a charger, think about the installation costs. Level 2 charging equipment and installation can cost about $2,000. Other costs might come up, like if you need to upgrade your electrical panel.
Using smart technology can help control costs. For example, smart EV charging stations can regulate power draw. This reduces the risk of overloading your main breaker.
| Charger Type | Original Price | Current Price |
|---|---|---|
| ChargePoint Home 25 Plug | $749.00 | $699.00 |
| Tesla Wall Connector (Gen 3) | $420.00 | $419.00 |
| Tesla Wall Connector (Gen 2, 8.5 Foot Cable) | $500.00 | $500.00 |
| Wallbox Pulsar Plus | Not provided | $699.00 |
| ClipperCreek HCS-50 | Not provided | Not provided |
If you want to use your EV as a backup power source, be ready for higher costs. This can reach up to $5,000. But, there are cheaper options like RVE Demand Charge Controllers. They manage when the charger works, based on your home’s electrical load.
Benefits of Public EV Charging Stations
Public EV charging stations offer big benefits for users and the planet. They make it easier for people to use electric cars, even if they can’t charge at home. These stations are found in places like malls, airports, and downtown areas where cars are parked for a while.
These stations help electric cars go farther, which means less gas is used. As more electric cars are expected to hit the roads, having enough charging spots is key.
Starting a public charging station can really help local businesses. In California, for example, it boosted spending by about $1,500 in 2019. This shows how public charging can help nearby businesses get more customers.
- Charging stations help local economies, even in tough areas.
- They make it easier for different types of vehicles to run efficiently.
- Utilities help fleets switch to electric cars.
- Rules like building codes and parking rules can encourage more charging spots.
But, there are still challenges. The U.S. needs up to 235,000 fast chargers soon. Businesses need to help build a big EV charging network. This helps not just car owners but the whole economy.
As more charging stations are built, it’s important to understand their benefits. By placing them well, we can make electric cars more appealing. This will help our communities grow in a green and strong way.
EV Charging Station Infrastructure Development
The growth of electric vehicles needs a strong network of charging stations. Federal initiatives help by funding the building of these networks. The National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure Formula Program is a key example, aiming to speed up the installation of charging stations nationwide.
Federal Support for Charging Networks
Federal support boosts the reach and reliability of EV charging. Grants and funding help create a broad network of charging points. The U.S. Department of Transportation estimates we’ll need about 12.9 million charge ports by 2030, making federal funding crucial.
State Level Initiatives and Incentives
States also offer incentives for EV charging stations. They provide tax credits, rebates, and grants to lower costs. For instance, installing a residential Level 2 charger costs about $1,300, while public ones cost around $2,500 per connector.
States also cover a big part of the labor costs, which decrease with bigger installations. This teamwork between federal and state governments helps grow the EV charging network. It makes using electric vehicles easier and more appealing.

Maintaining and Troubleshooting EV Charging Stations
Keeping EV chargers in good shape is key to their reliability and ease of use. Regular checks can spot problems early. These checks should look at the hardware, electrical connections, and software updates.
When fixing charging stations, common issues pop up. For example, if the power is low, it might mean a hardware problem or electrical issue. A simple checklist can help troubleshoot these problems.
- Checking for error messages on the charger display.
- Inspecting cables for damage or wear.
- Confirming power supply continuity.
- Testing the charger with different vehicle models.
Studies show that owners should budget around $400 a year for each charger’s upkeep, not counting electricity costs. DC fast chargers might need more, up to $800 a year, because of their complex parts.
Looking at how often chargers are used is crucial for fixing them and managing them well. Tracking charging events shows how well they work and if prices are right. Landlords can also get help from the New York State Energy Research and Development Authority to figure out if charging stations are profitable.
Not fixing chargers fast enough can mean not following new rules from the Biden administration. These rules require chargers to be up and running 97% of the time. Following these rules makes sure chargers work well and keeps investments safe.
| Charging Station Type | Average Annual Maintenance Cost | Break-Even Charging Events/Day |
|---|---|---|
| Level 2 Charger | $400 | Depends on pricing model |
| DC Fast Charger | $800+ | Higher due to initial costs |
By planning well for EV charger upkeep and using good troubleshooting, operators can offer reliable service. This meets the growing need for EV charging spots across the country.
Conclusion
This guide gives a detailed look at EV charging and its importance for green transport. With electric cars becoming more popular, we need more charging spots. By 2024, the US has over 200,000 charging ports, but we’ll need even more.
Companies like Legrand are key in growing our charging networks. These networks are crucial for the increasing number of electric cars. The bipartisan infrastructure bill aims to invest in these networks, making our future greener.
Adding electric cars to our energy system helps fight climate change. It also starts a new era of transport that’s good for the planet and the economy. Moving forward with EV infrastructure is essential for a sustainable and prosperous future.
Leave a Reply